How to create a ERC-20 token and deploy it to the Ethereum network
June 7, 2022-6 min read
Let's keep building on the project setup that we did in the post Setup a Solidity project using Hardhat and Typescript. We will create a ERC-20 smart contract and deploy it on the Ethereum network.
What is ERC-20
ERC-20 tokens are blockchain-based assets that have value and can be sent and received. The primary difference to native coins like Bitcoin and Litecoin is that instead of running on their own blockchain, ERC-20 tokens are issued on the Ethereum network.
ERC stands for "Ethereum Request for Comments", which is an official protocol used to propose improvements to the Ethereum network. The "20" is the unique ID number used to identify the proposal.
ERC-20 is a technical standard for tokens issued on the Ethereum blockchain, providing a list of rules that all Ethereum-based tokens must follow. These standards include how the tokens can be transferred, how transactions are approved, how users can access data about a token, and the total supply of tokens.
All Smart Contracts that implement the following methods and events are considered ERC-20 tokens:
Methods
function name() public view returns (string)function symbol() public view returns (string)function decimals() public view returns (uint8)function totalSupply() public view returns (uint256)function balanceOf(address _owner) public view returns (uint256 balance)function transfer(address _to, uint256 _value) public returns (bool success)function transferFrom(address _from, address _to, uint256 _value) public returns (bool success)function approve(address _spender, uint256 _value) public returns (bool success)function allowance(address _owner, address _spender) public view returns (uint256 remaining)
Events
event Transfer(address indexed _from, address indexed _to, uint256 _value)event Approval(address indexed _owner, address indexed _spender, uint256 _value)
These functions are integral for user/token implementation, specifically in determining the amount of tokens in circulation, storing and returning balances, making transfer and withdrawal requests and granting approval, and agreeing to automated transfers.
Sample implementations
There are already plenty of ERC-20 compliant tokens deployed on the Ethereum network. Different implementations have been written by various teams that have different trade-offs: from gas saving to improved security.
Check these sample implementations:
Creating the token
We are going to extend on the OpenZeppelin implementation to build our own token. OpenZeppelin contracts are battle tested and used by many successful projects.
Install OpenZeppelin contracts
First, we have to install the OpenZeppelin dependency on our project:
$ npm install --save-dev @openzeppelin/contracts
Writing the smart contract
The contract source code should be inside the /contracts folder of our project:
TutorialToken.sol
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MITpragma solidity ^0.8.0;import "@openzeppelin/contracts/token/ERC20/ERC20.sol";contract TutorialToken is ERC20 {constructor(uint256 initialSupply) ERC20("Tutorial", "TUT") {_mint(msg.sender, initialSupply);}}
First, we import the OpenZeppelin ERC20.sol contract. Then, we create a contract called TutorialToken that extends the ERC20 contract. We then define a constructor for our contract, which is also indicating the arguments for the constructor of the base contract; the name of the token and it's symbol. Finally, we are minting some tokens and giving them to the address that deploys the smart contract.
The base contract ERC20.sol provided by OpenZeppelin is implementing all the methods and events we mentioned above. We don't have to implement anything more ourselves.
Compile the smart contract using npx hardhat compile:
Generating typings for: 5 artifacts in dir: typechain for target: ethers-v5Successfully generated 11 typings!Compiled 5 Solidity files successfully
Add some unit tests
This is an optional step of course, but it's always important to have some tests covering your smart contracts. We'll use chai-as-promised to add some syntactic sugar to our tests:
$ npm install --save-dev @types/chai-as-promised chai-as-promised
TutorialToken.test.ts
import { ethers } from "hardhat";import chai from "chai";import chaiAsPromised from "chai-as-promised";import { TutorialToken } from "../typechain/TutorialToken";import { TutorialToken__factory } from "../typechain/factories/TutorialToken__factory";import { Signer } from "ethers";chai.use(chaiAsPromised);const { expect } = chai;describe("TutorialToken", () => {let tutorialTokenFactory: TutorialToken__factory;let tutorialToken: TutorialToken;describe("Deployment", () => {let deployer: Signer;beforeEach(async () => {[deployer] = await ethers.getSigners();tutorialTokenFactory = new TutorialToken__factory(deployer);tutorialToken = await tutorialTokenFactory.deploy(100);await tutorialToken.deployed();});it("should have the correct name", async () => {expect(await tutorialToken.name()).to.equal("Tutorial");});it("should have the correct symbol", async () => {expect(await tutorialToken.symbol()).to.equal("TUT");});it("should have the correct total supply", async () => {expect((await tutorialToken.totalSupply()).toString()).to.equal("100");});it("should have correct balance after deployment", async () => {expect(await tutorialToken.balanceOf(await deployer.getAddress())).to.equal("100");});});});
Execute the tests using npx hardhat test:
TutorialTokenDeployment✔ should have the correct name✔ should have the correct symbol✔ should have the correct total supply✔ should have correct balance after deployment
Deploying on the Ethereum network
With our contract tested, we are ready to deploy it to the Ethereum network. Specifically, we will deploy on the Goerli testnet and not on the mainnet.
Get API key from alchemyapi.io
To interact with the Ethereum network we need a node running locally. Alternative, we can access the network via HTTPS using third party services, like Infura or Alchemy. We will use the latter.
Sign up for a free account on Alchemy and create a new App on the Ethereum chain and the Goerli network. After this, you'll be able to get an API key for your app.
Get ETH from faucet
You'll also need some ETH on your wallet because deploying a smart contract is a transaction that has a gas cost. Luckilly there is a faucet for the Goerli netowrk that can provide you with ETH 0.05 per day.
Add test net to hardhat config
Create a .env file in the root of the project, and add the following:
GOERLI_URL=https://eth-goerli.alchemyapi.io/v2/<Your alchemy api key>PRIVATE_KEY=<Your ethereum address private key>
On the hardhat.config.ts file, add an entry for the Goerli network:
networks: {goerli: {url: process.env.GOERLI_URL || "",accounts:process.env.PRIVATE_KEY !== undefined ? [process.env.PRIVATE_KEY] : [],},},
Deploy
This will be our deployment script. Notice that we are passing the number of tokens that will be minted to us in the constructor of the token
deploy.ts
import { ethers } from "hardhat";async function main() {const tutorialTokenFactory = await ethers.getContractFactory("TutorialToken");const tutorialToken = await tutorialTokenFactory.deploy(ethers.utils.parseUnits("100"));await tutorialToken.deployed();console.log("TutorialToken deployed to:", tutorialToken.address);}main().catch((error) => {console.error(error);process.exitCode = 1;});
Finally, everything is now ready for the contract deployment:
$ npx hardhat run --network goerli scripts/deploy.ts
Verify
After the deployment script has executed, it will print the address where the contract was deployed to:
TutorialToken deployed to: 0x32d6CBF133A80d3dd959DbdB41b8E41FD4831EF0
you can verify that the contract is deployed by visiting etherscan, at https://goerli.etherscan.io/token/<the contract address>
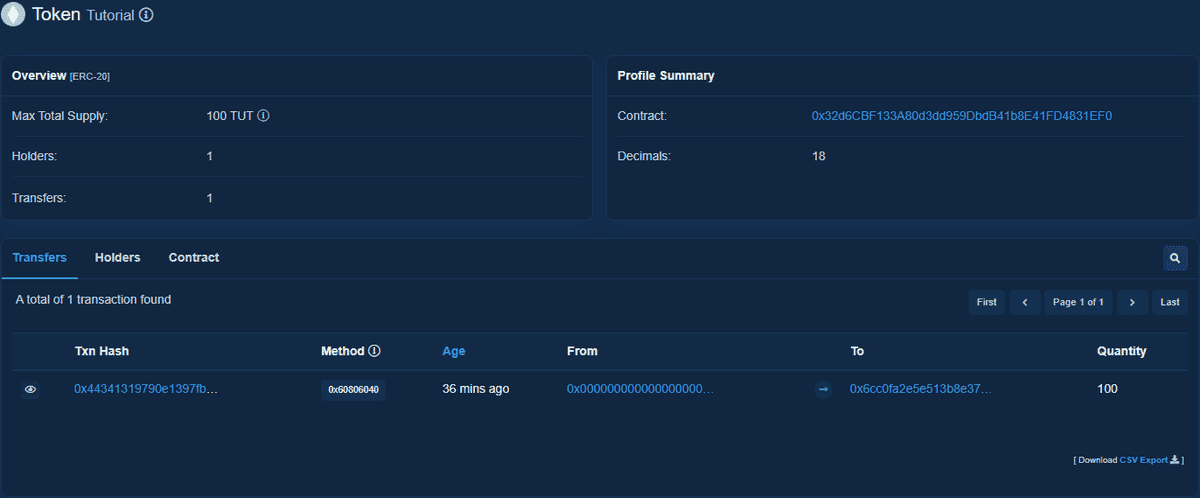
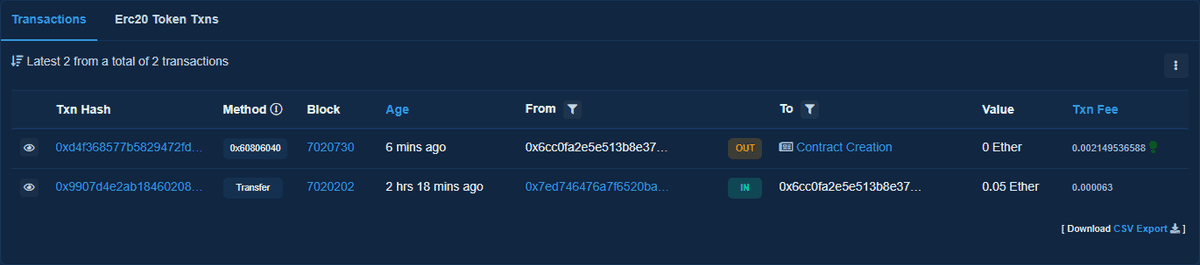
You can also check your address at https://goerli.etherscan.io/address/<your address>.
On the Transactions tab, you can see the transaction that created the contract.
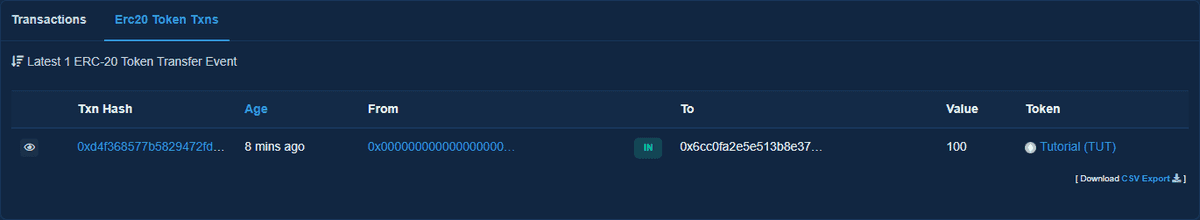
On the ERC-20 Tokens tab, you can see that your address now has 100 TUT tokens.
Sources
Sources for this tutorial can be found here.
